Intel “Raptor Lake” Rumored to Feature Massive Cache Size Increases
[ad_1]
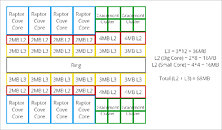
The “Raptor Lake-S” silicon is expected to feature eight “Raptor Cove” P-cores, and four “Gracemont” E-core clusters (each cluster amounts to four cores). The “Raptor Cove” core is expected to feature 2 MB of dedicated L2 cache, an increase over the 1.25 MB L2 cache per “Golden Cove” P-core of “Alder Lake-S.” In a “Gracemont” E-core cluster, four CPU cores share an L2 cache. Intel is looking to double this E-core cluster L2 cache size from 2 MB per cluster on “Alder Lake,” to 4 MB per cluster. The shared L3 cache increases from 30 MB on “Alder Lake-S” (C0 silicon), to 36 MB on “Raptor Lake-S.” The L2 + L3 caches hence add up to 68 MB. All eyes are now on “Zen 4,” and whether AMD gives the L2 caches an increase from the 512 KB per-core size that it’s consistently maintained since the first “Zen.”
[ad_2]